Fatty Acid Synthesis- Lecture 2 (Acetyl CoA Carboxylase)
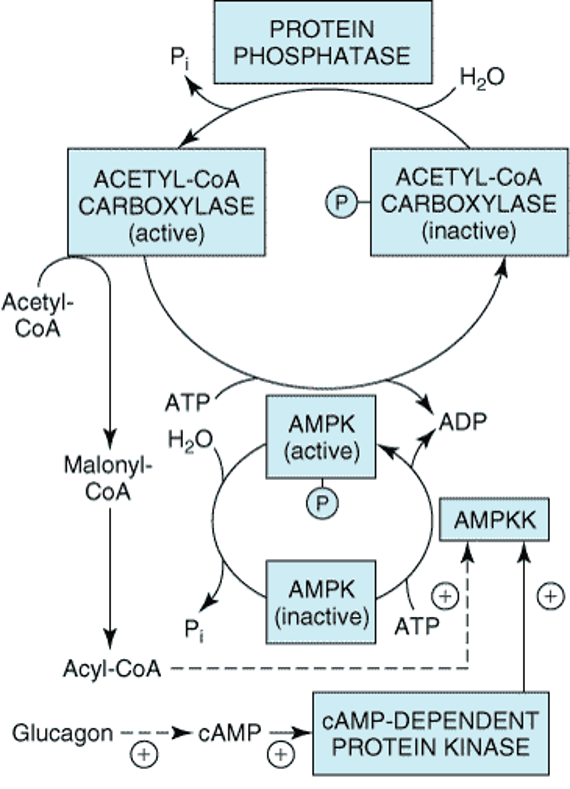
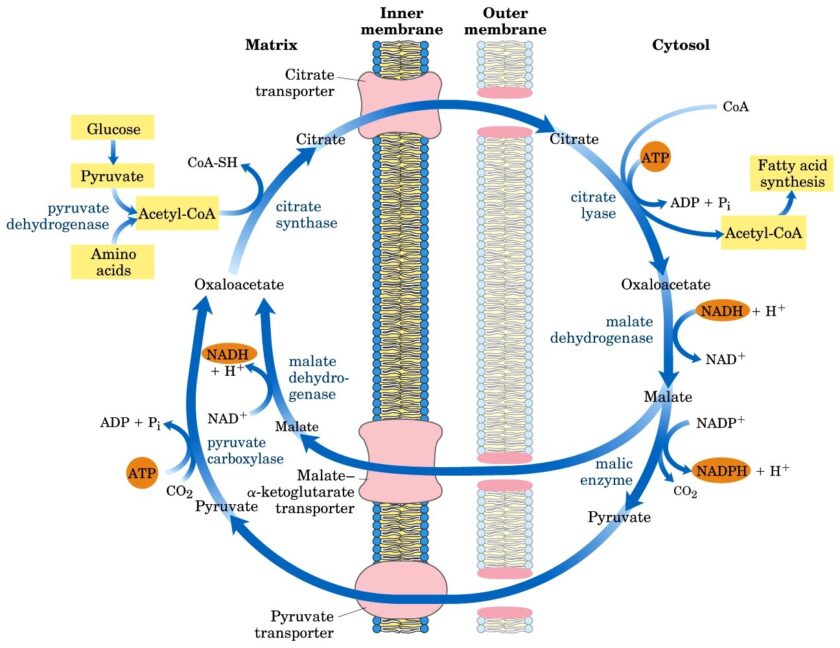
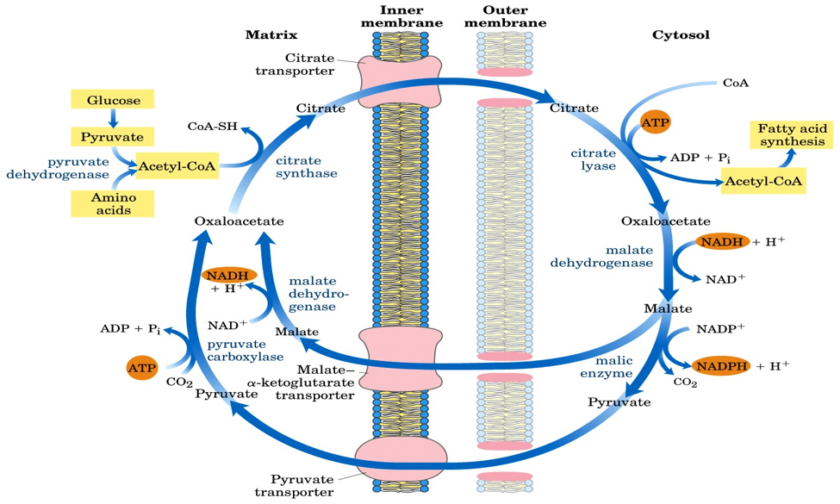
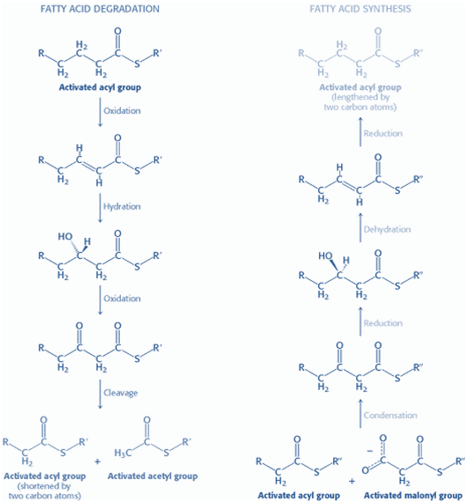
The fatty acid synthesis starts with the carboxylation of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA. This irreversible reaction is the committed step in fatty acid synthesis (figure 1). Figure- 1- Showing the formation of Malonyl Co A from Acetyl Co A Bicarbonate as a source of CO2 is required in the initial reaction for the carboxylation […]
Fatty Acid Synthesis- Lecture 2 (Acetyl CoA Carboxylase) Read More »