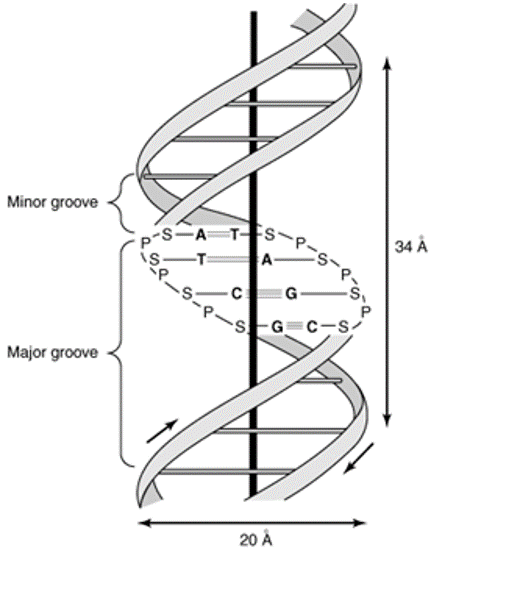
DNA Damage And Repair
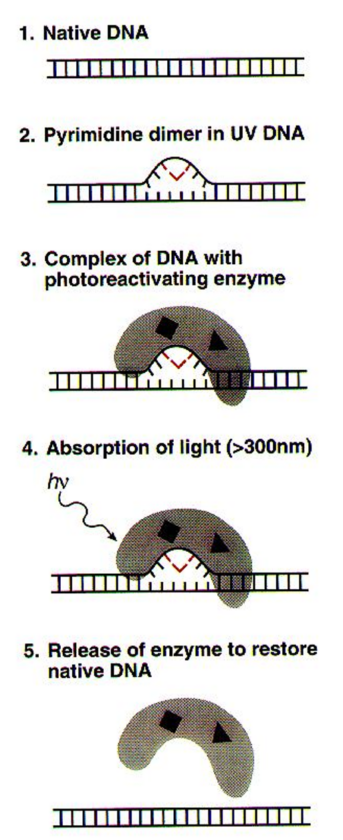
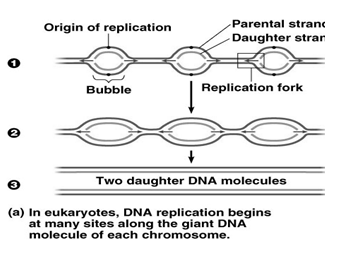
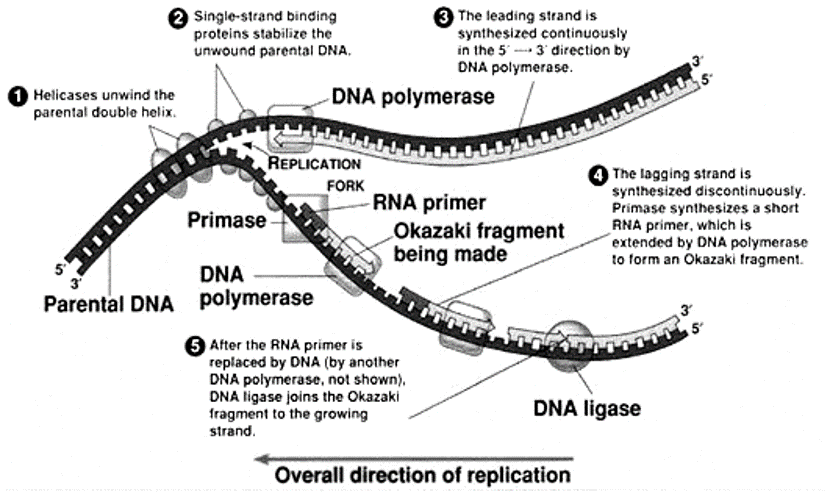
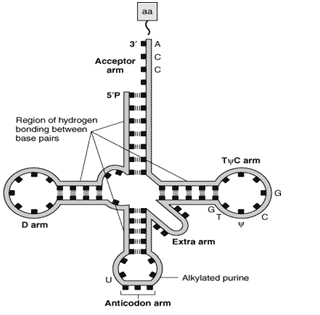
DNA in the living cell is subjected to many chemical alterations. If the genetic information encoded in the DNA is to remain uncorrupted, any chemical changes must be corrected. A failure to repair DNA produces a mutation. Agents that Damage DNA Radiations- Highly reactive oxygen radicals produced during normal cellular respiration as well as by other biochemical pathways Ionizing […]
DNA Damage And Repair Read More »