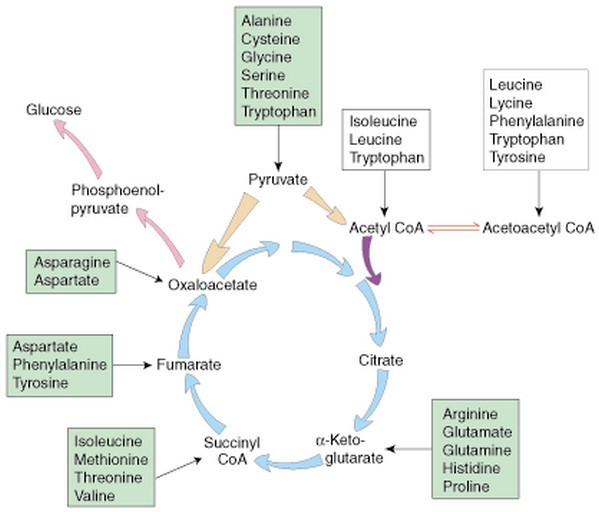
Glycogen storage diseases with mnemonics to aid memorization
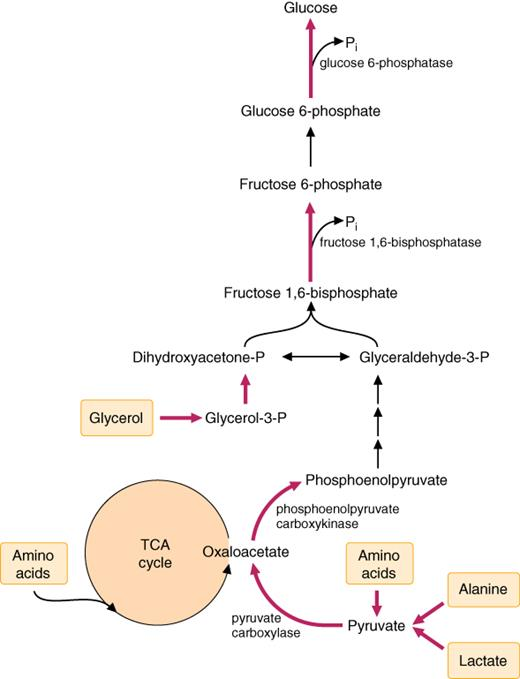
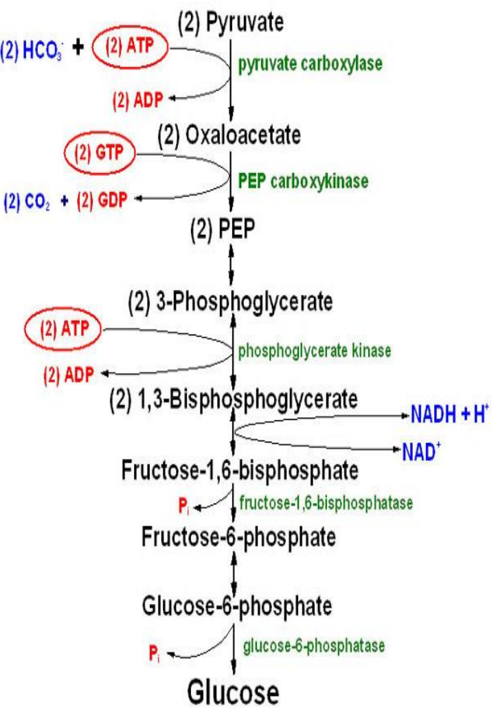
A table summarizing the main glycogen storage diseases (GSDs) with enzyme defects, key clinical features, and mnemonics to aid memorization: Glycogen Storage Disease Enzyme Defect Key Clinical Features Mnemonic Type I: von Gierke Disease (GSD I) Glucose-6-phosphatase Severe fasting hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia “von Gierke: ‘G6P’s Gone, Liver Left Low” Type II: Pompe […]
Glycogen storage diseases with mnemonics to aid memorization Read More »