Alcohol Induced Metabolic Changes- A Case Study
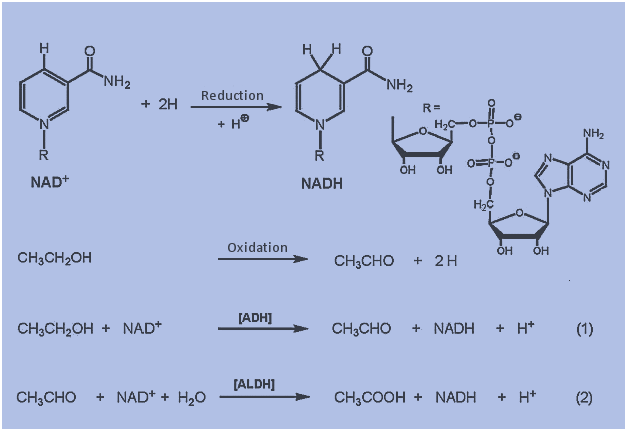
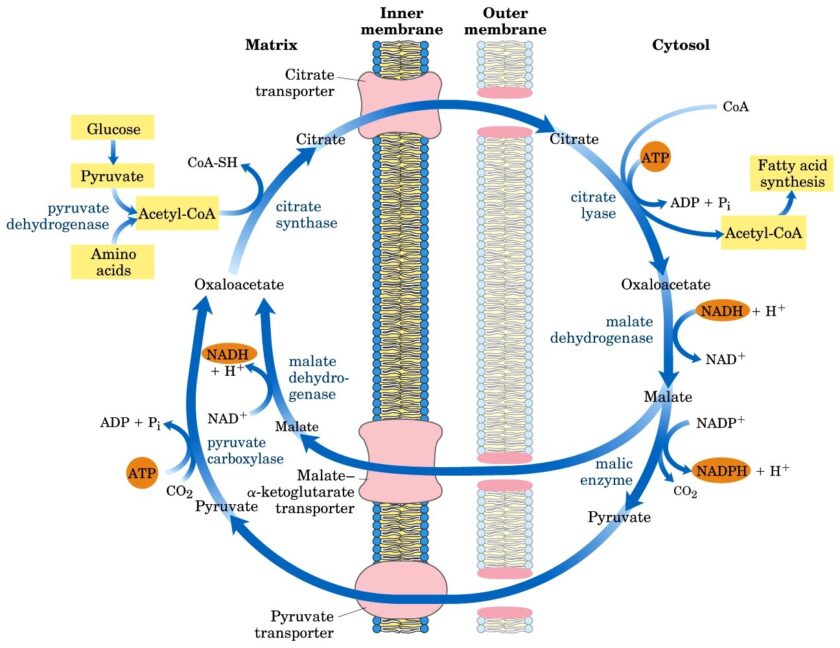
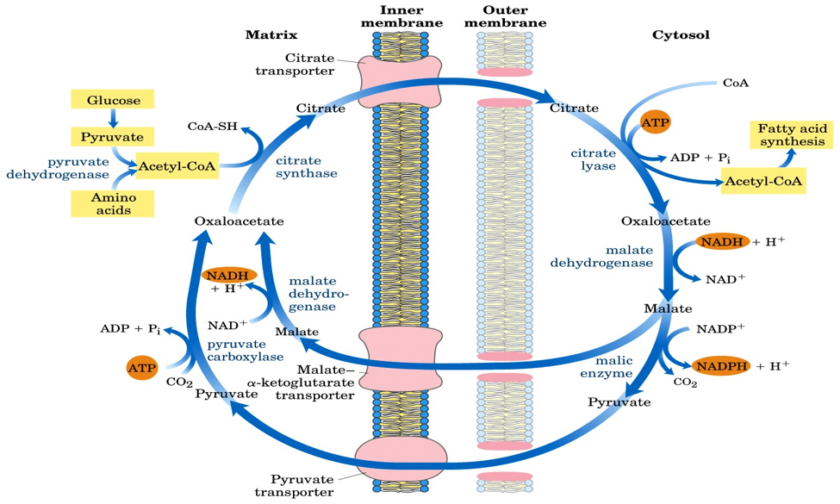
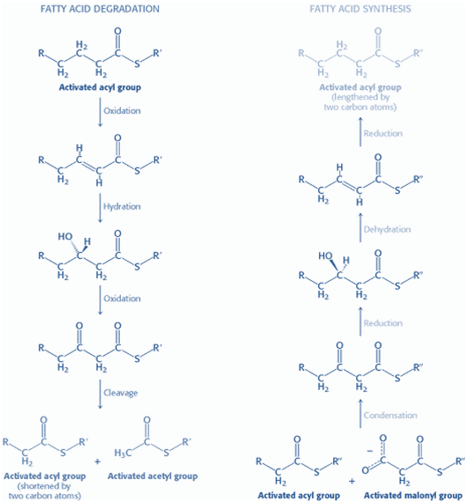
Case details A 65-year-old man was admitted to the emergency department in an unconscious state. Apparently, he had become increasingly depressed after the death of his younger son two months ago. Previously, before his death, he had been a moderate drinker, but consumption of alcohol had increased markedly over the last few weeks. He had […]
Alcohol Induced Metabolic Changes- A Case Study Read More »