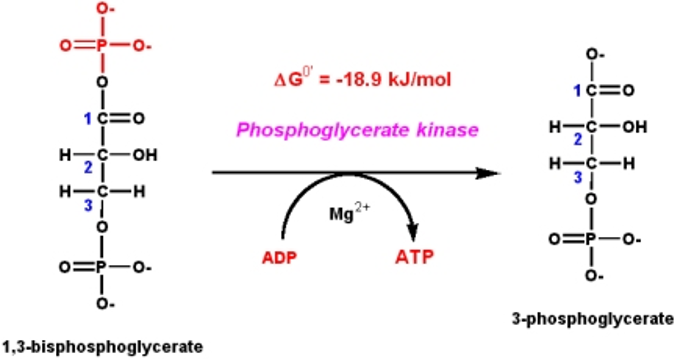
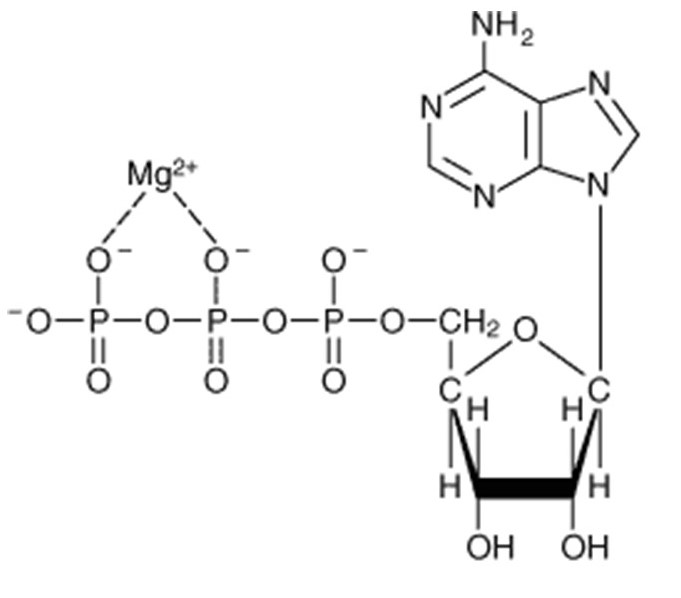
Structure, sources and functions of ATP
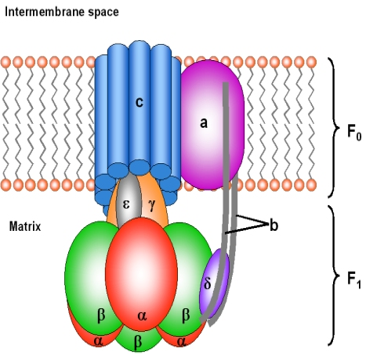
ATP- Energy Currency of cell The nucleotide coenzyme adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most important form of chemical energy in all cells. All fuel sources of Nature, all foodstuffs of living things, produce ATP, which in turn powers virtually every activity of the cell and organism. The cleavage of ATP is strongly exergonic. The energy […]
Structure, sources and functions of ATP Read More »