“Master Transcription with Case-Based MCQs: Test Your Understanding!”
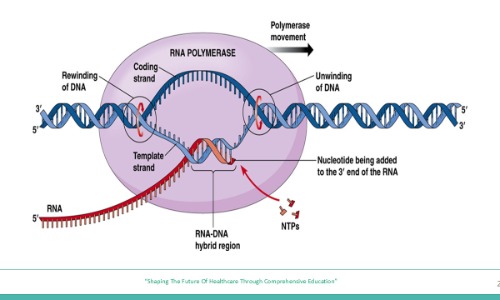
1. A previously healthy 8-year-old develops symptoms of fatigue and anemia. Bone marrow biopsy reveals decreased erythropoiesis, and further molecular analysis shows that the transcription of β-globin mRNA is markedly reduced due to a defect in the assembly of the pre-initiation complex. However, RNA polymerase II is intact and enzymatically functional. Which of the following […]
“Master Transcription with Case-Based MCQs: Test Your Understanding!” Read More »