Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation- Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations-Set-2
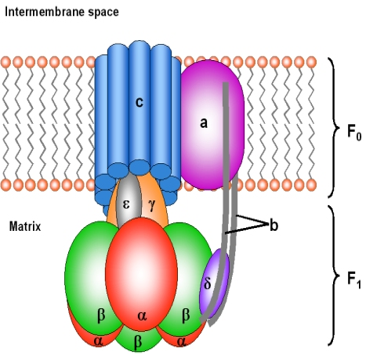
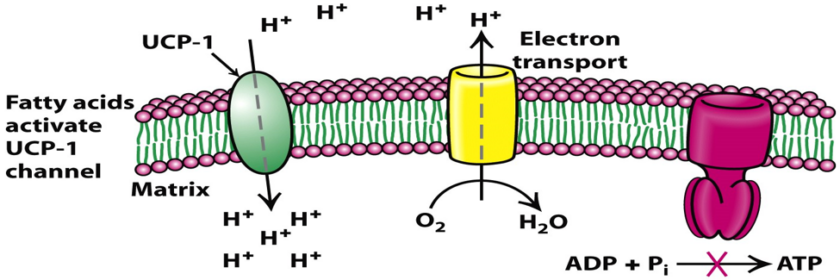
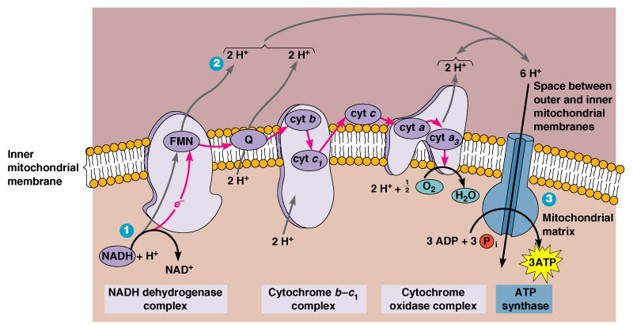
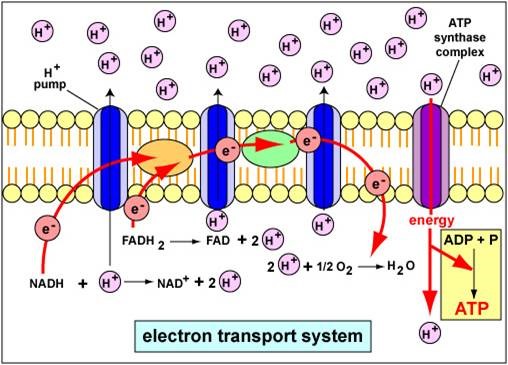
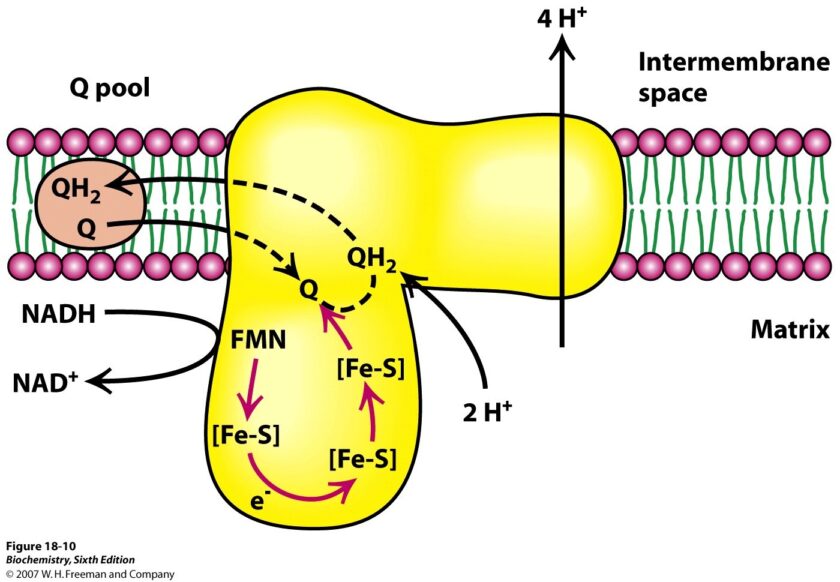
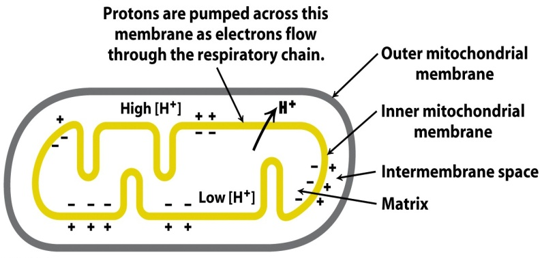
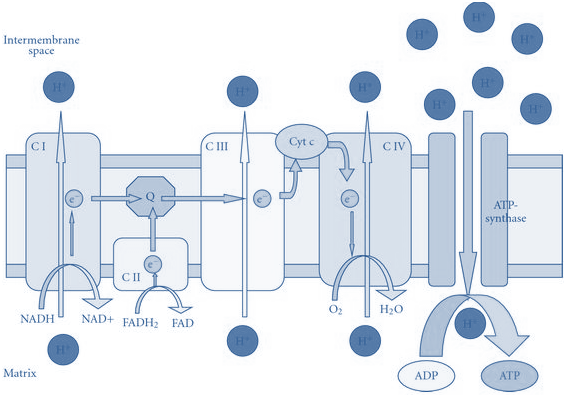
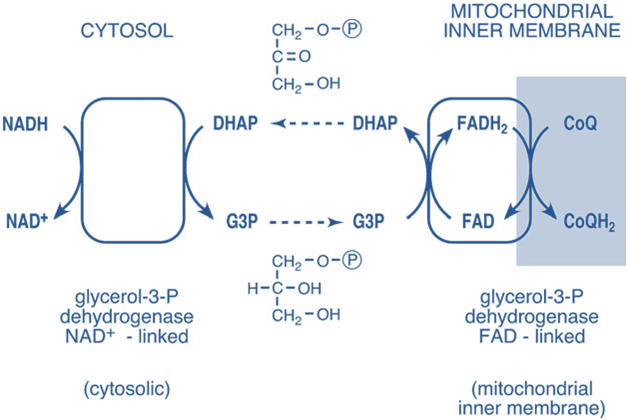
11. A 48-year-old patient is brought to the emergency room after exposure to toxic fumes suspected to contain cyanide. He presents with shortness of breath, confusion, and metabolic acidosis. The medical team suspects cyanide toxicity, which disrupts the electron transport chain (ETC). Which of the following statements concerning the components of the electron transport chain […]