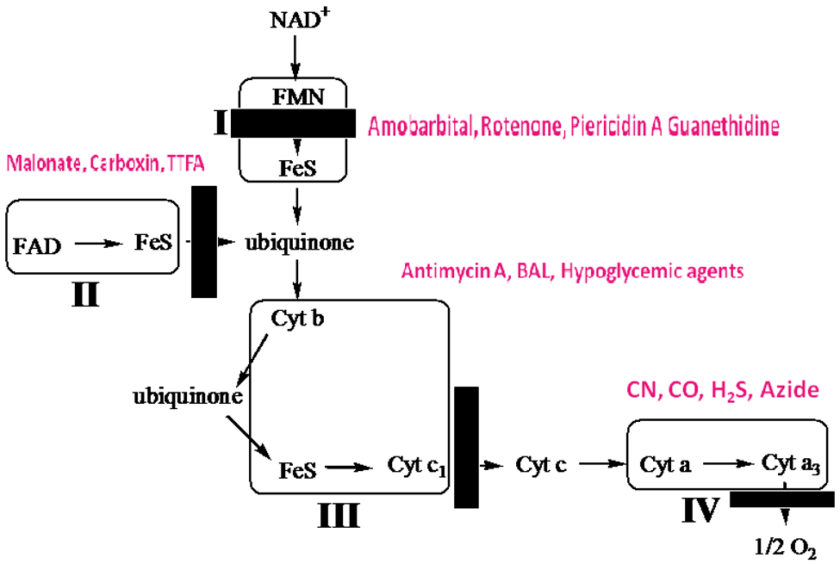
Electron Transport Chain -strictly aerobic (a brief review)
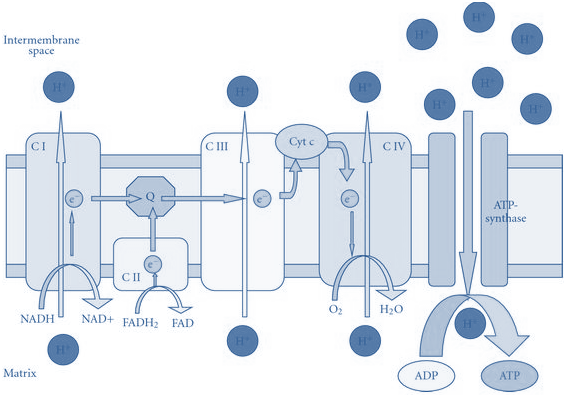
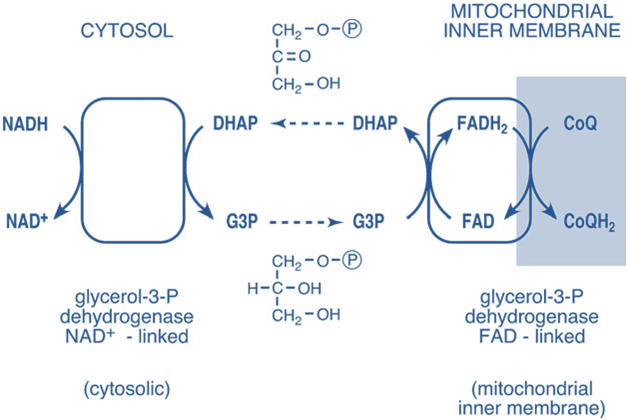
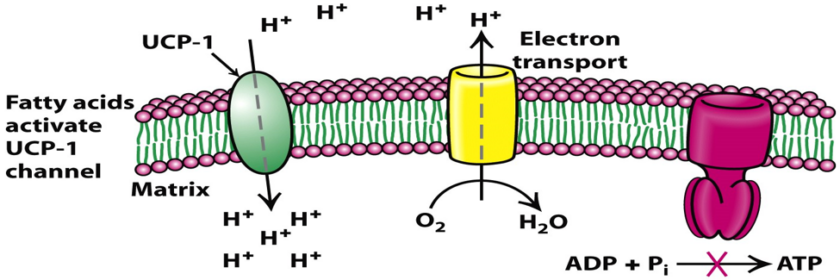
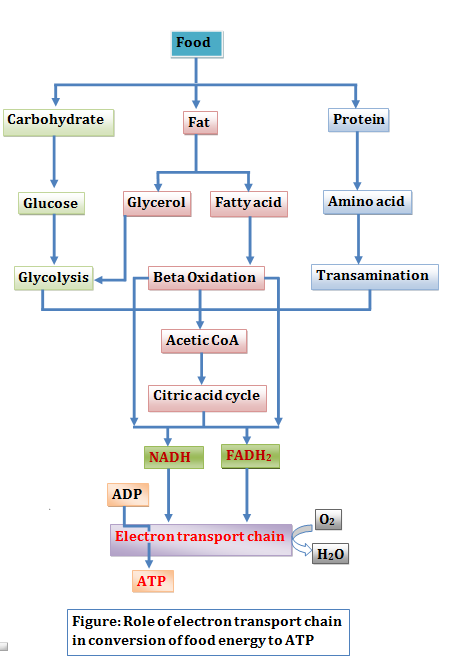
Introduction Most of the energy liberated during the oxidation of carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids are made available within mitochondria as reducing equivalents (—H or electrons). The NADH and FADH2 formed in glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and the citric acid cycle are energy-rich molecules because each contains a pair of electrons having a high […]
Electron Transport Chain -strictly aerobic (a brief review) Read More »