Vitamin Deficiencies and Impairments in Carbohydrate Metabolism
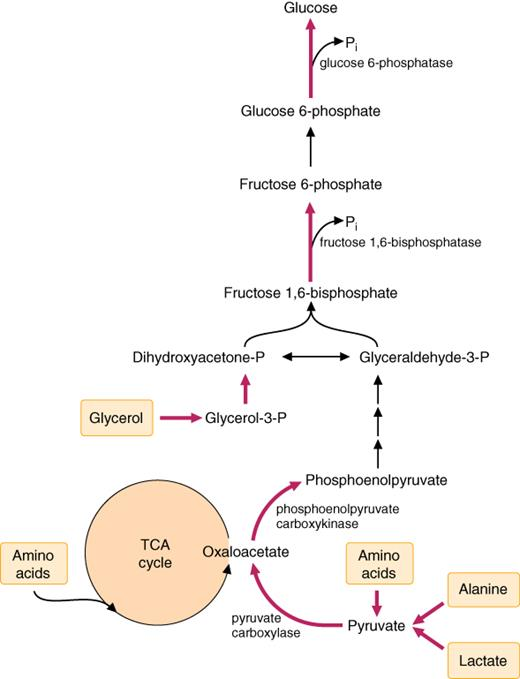
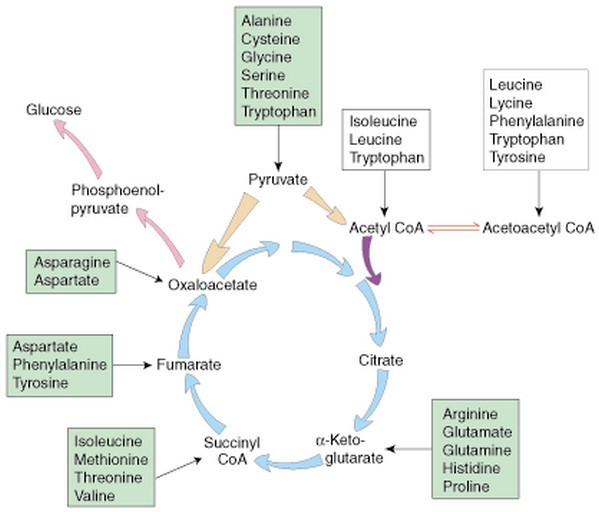
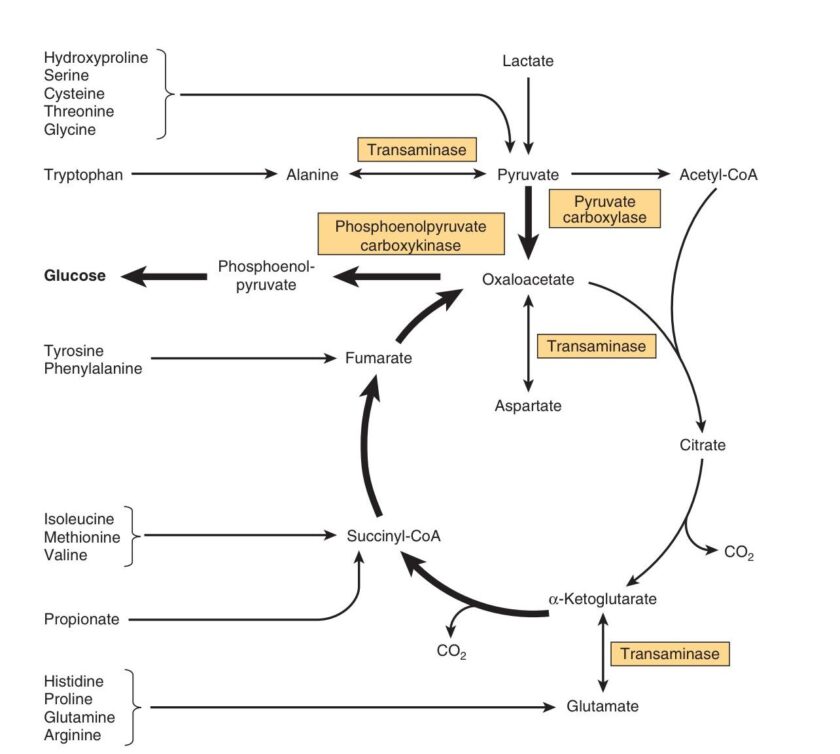
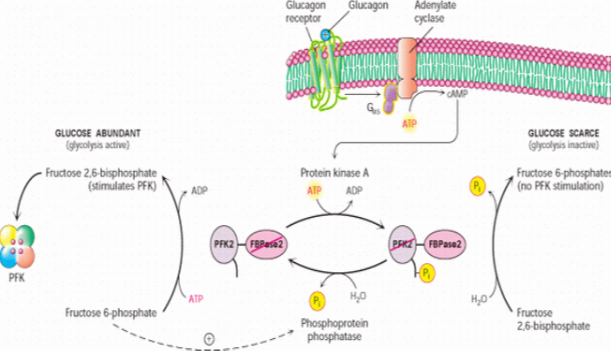
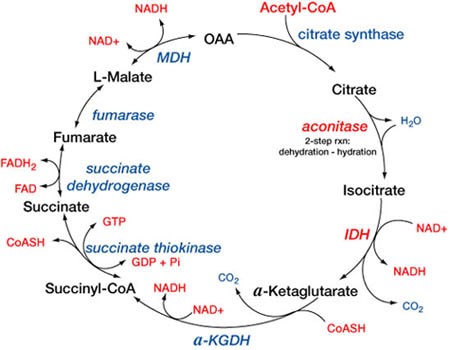
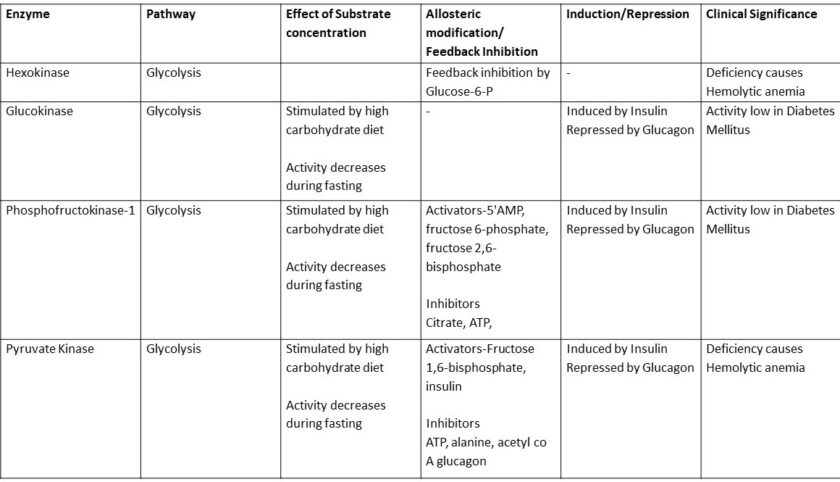
“Vitamins play essential roles in carbohydrate metabolism by acting as coenzymes or precursors for enzymes. Deficiencies in vitamins like Thiamine, Riboflavin, and Niacin can impair critical biochemical reactions, such as the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA or oxidation in the TCA cycle, leading to conditions like lactic acidosis and energy deficits. Discover the intricate biochemical pathways affected and their physiological impacts in our detailed analysis.”
Vitamin Deficiencies and Impairments in Carbohydrate Metabolism Read More »