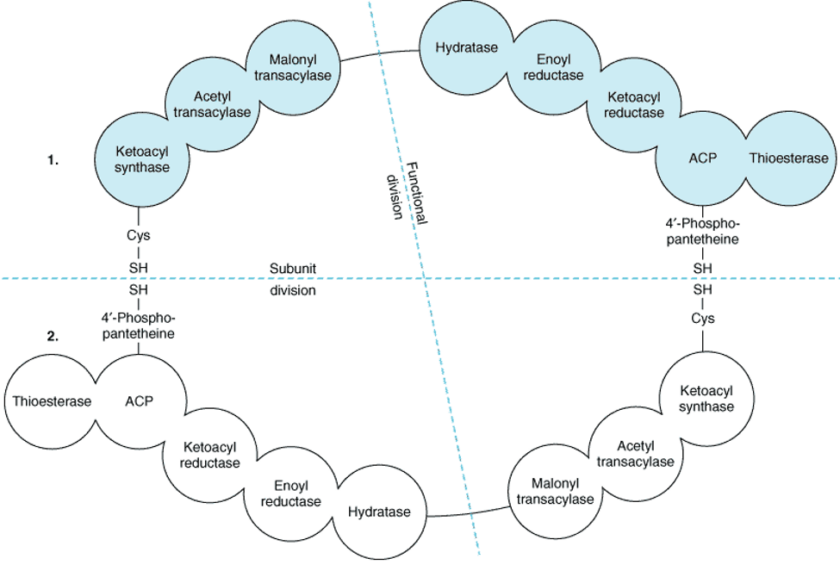
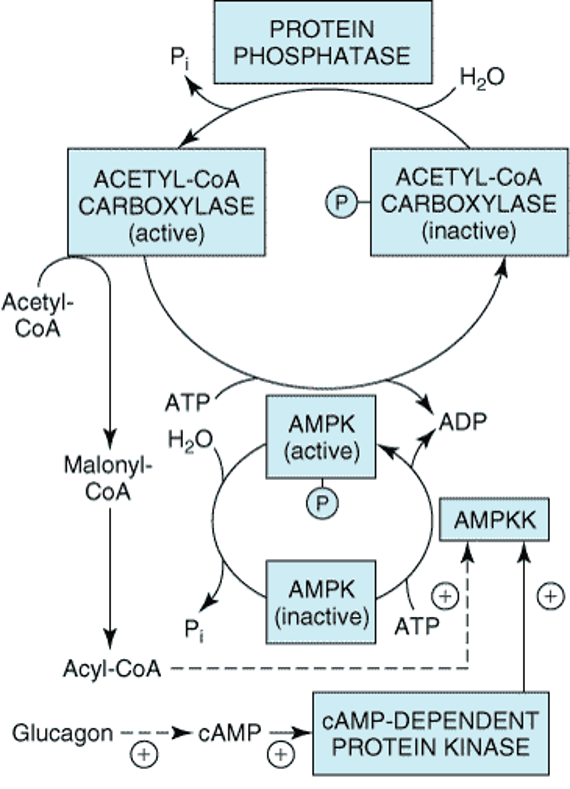
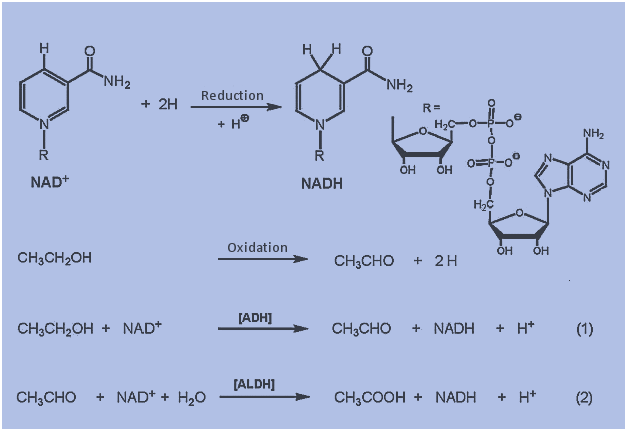
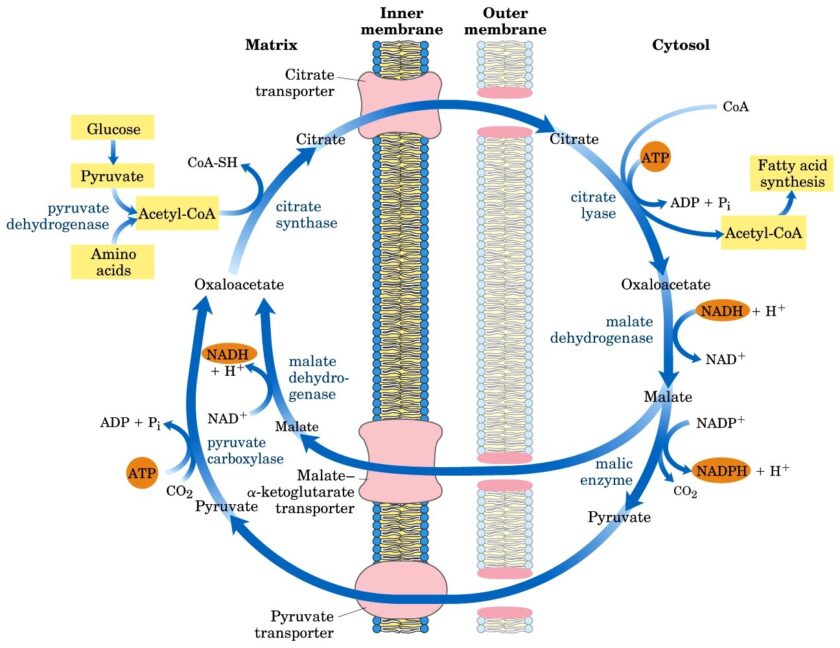
Ketogenesis-lecture 2
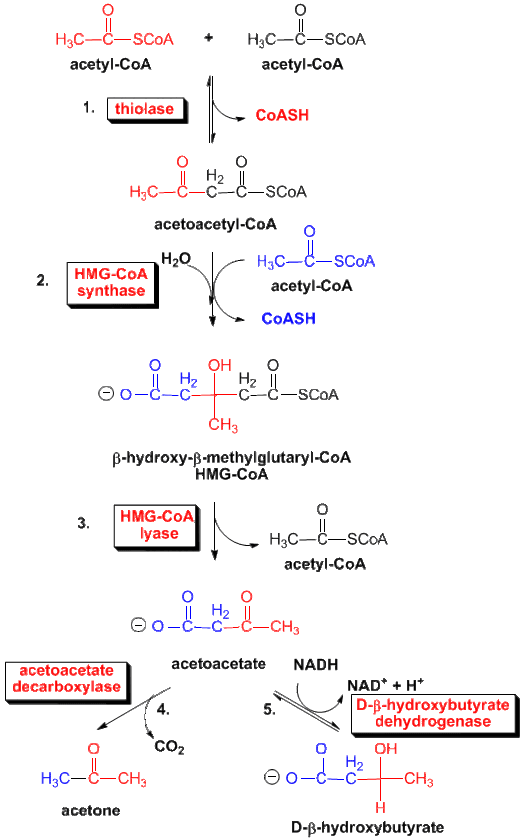
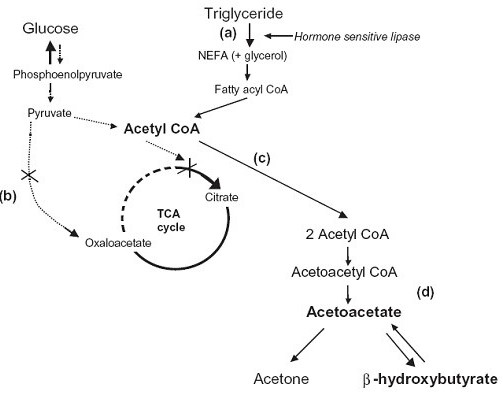
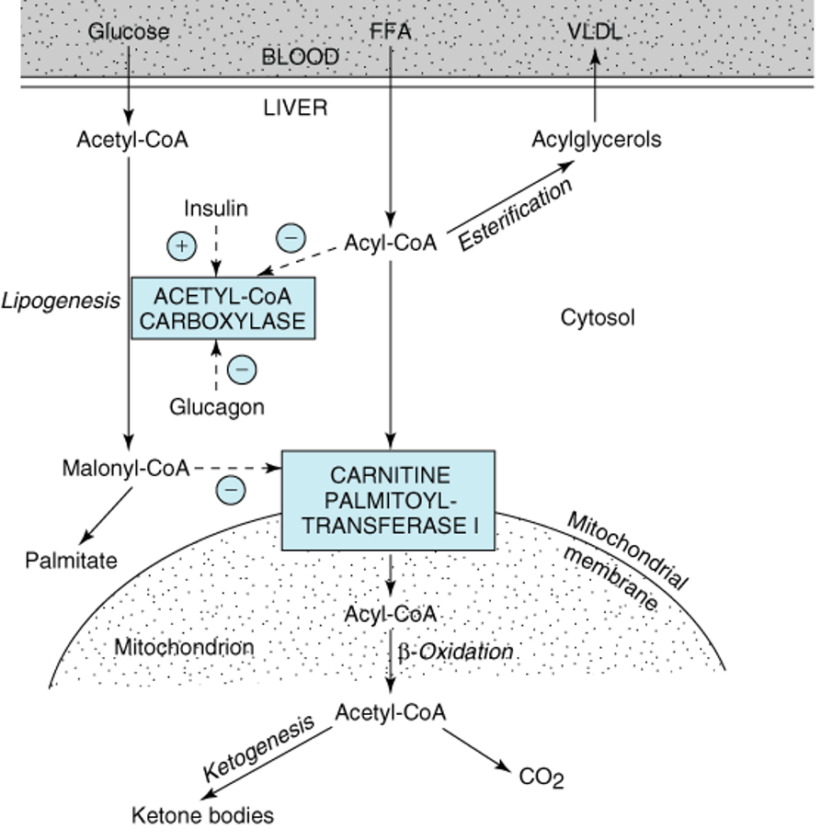
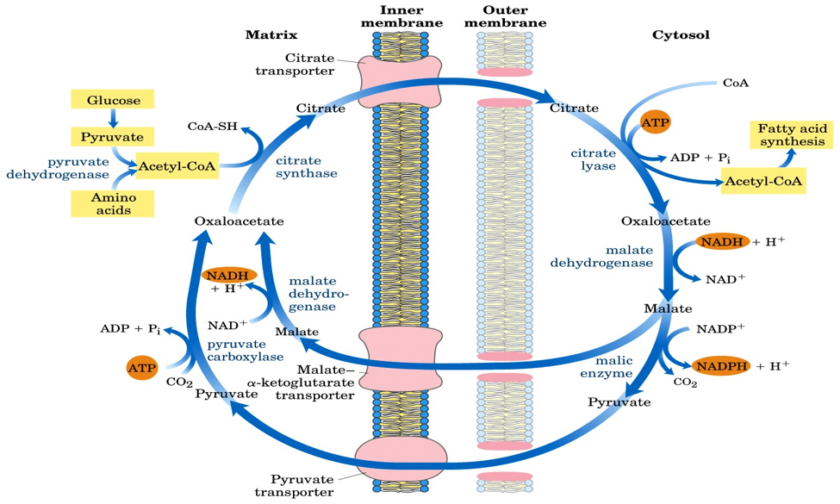
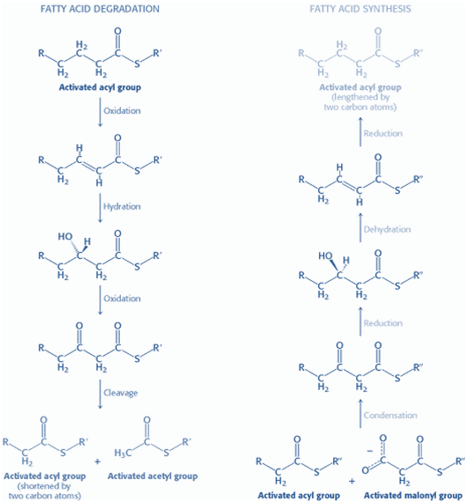
Ketogenesis Ketogenesis takes place in the liver using Acetyl CoA as a substrate or a precursor molecule. Enzymes responsible for ketone body formation are associated mainly with the mitochondria. Steps of synthesis-Acetoacetate (the first ketone body) is formed from acetyl CoA in three steps (figure ). 1)Two molecules of acetyl CoA condense to form Acetoacetyl […]
Ketogenesis-lecture 2 Read More »