Minor pathways of oxidation of fatty acids- Lecture-1 (Alpha-oxidation)
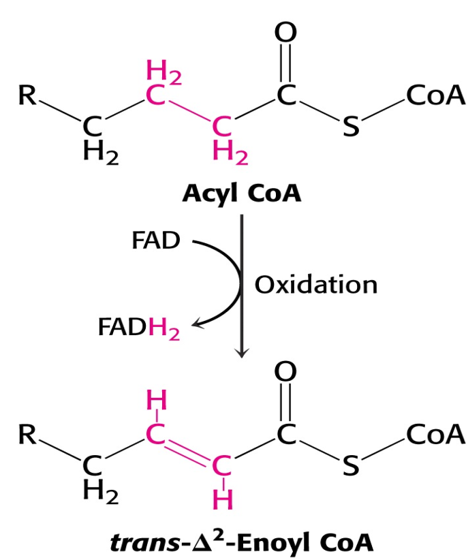
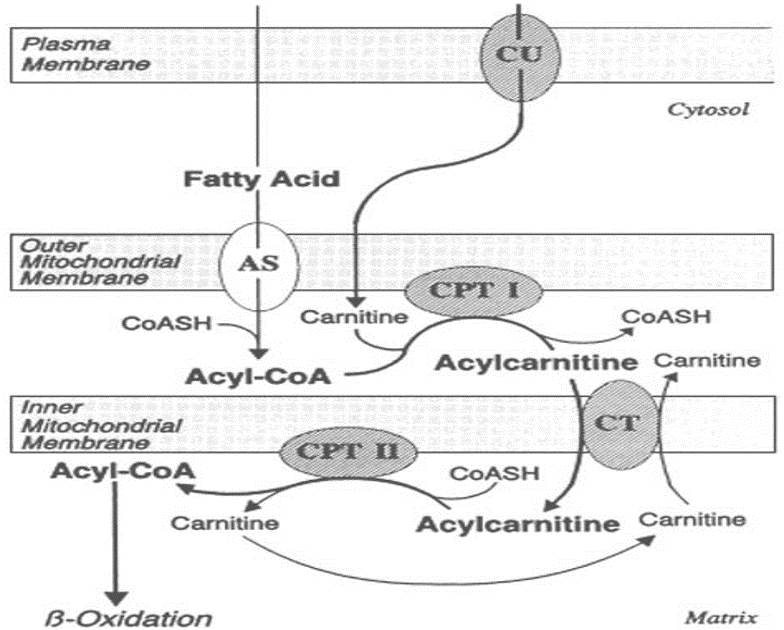
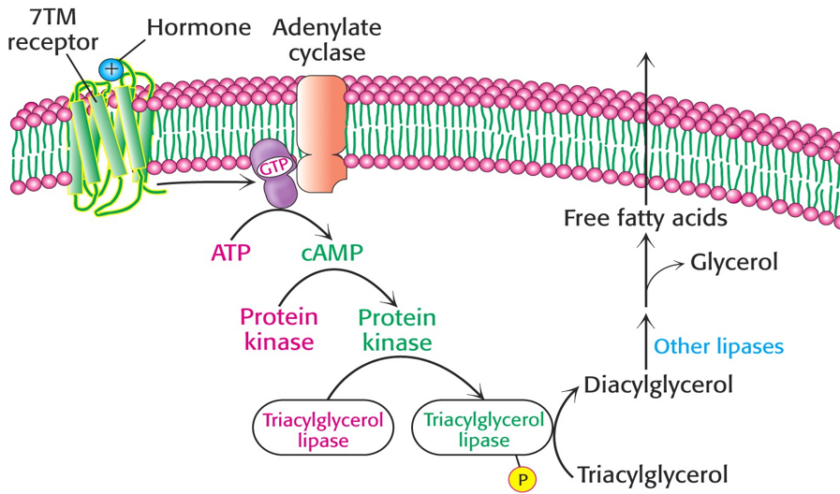
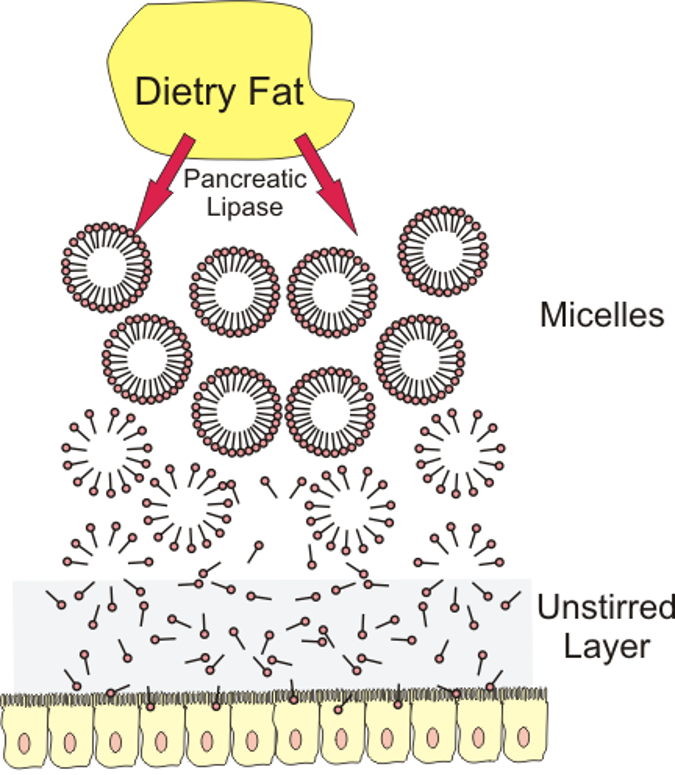
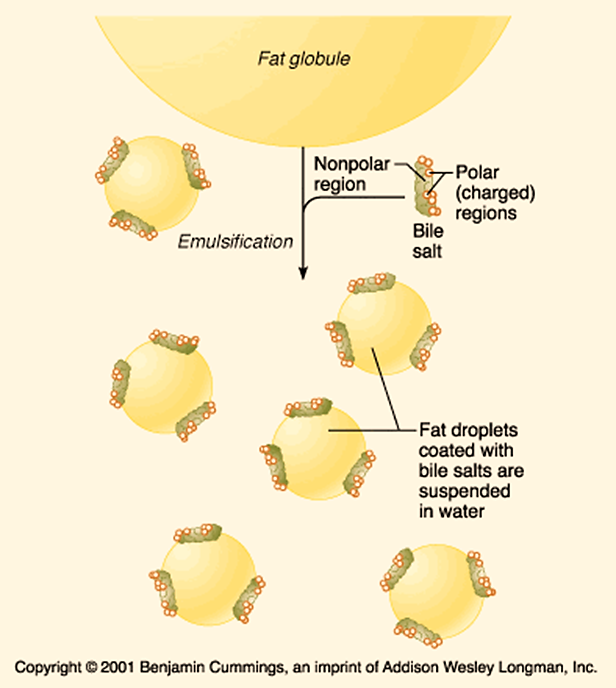
The β oxidation accounts for the bulk of energy production from fatty acids in humans. These reactions must be supplemented by other mechanisms so that all types of ingested fatty acids can be oxidized. Overview of minor pathways of the biological importance of fatty acid oxidation 1) α- Oxidation- Oxidation occurs at C-2 instead of […]
Minor pathways of oxidation of fatty acids- Lecture-1 (Alpha-oxidation) Read More »