Ammonia Disposal – Short-answer questions
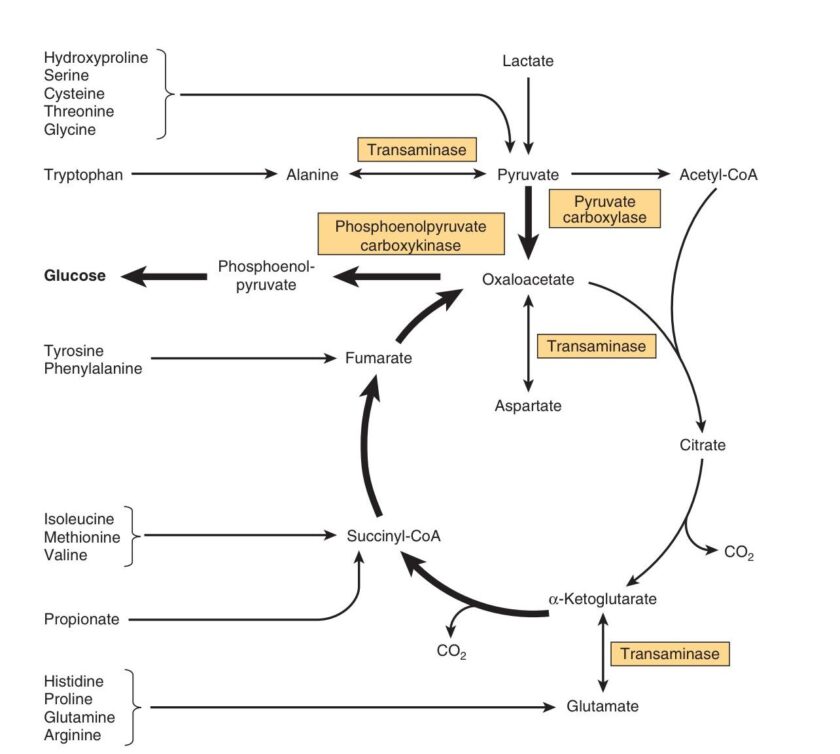
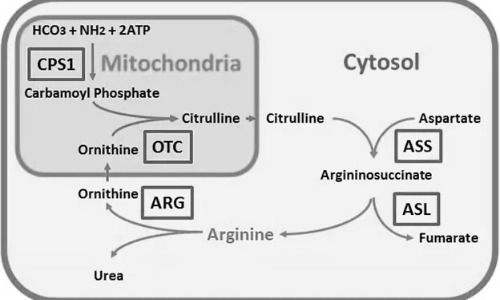
Question 1: What is the primary function of the urea cycle in humans? Answer: The urea cycle converts ammonia, a highly toxic byproduct of amino acid metabolism, into urea, a less toxic compound that can be safely excreted in urine. This process is vital for maintaining nitrogen balance in the body. Question 2: Which cellular […]
Ammonia Disposal – Short-answer questions Read More »