Types of Enzyme Inhibition with Mnemonics
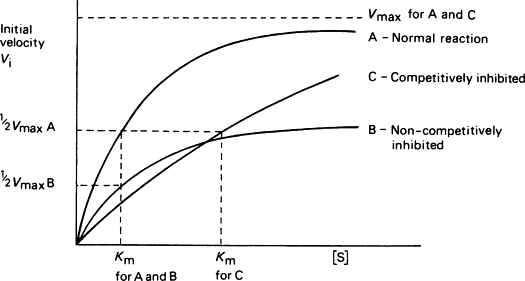
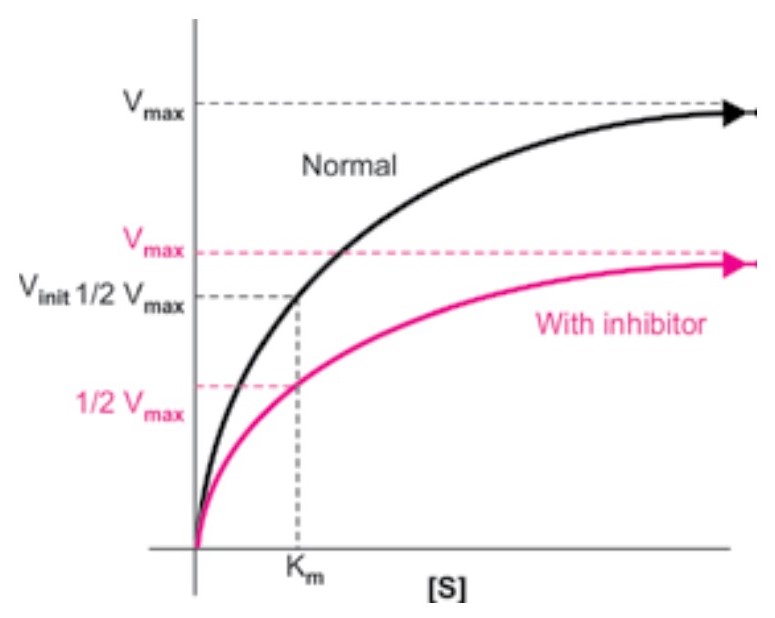
Type of Inhibition Effect on Vmax and Km Reversible / Irreversible Examples Mnemonic Competitive (Inhibitor competes with substrate for the active site) Vmax: Unchanged Km: Increased Reversible 1) Statins – inhibit HMG-CoA Reductase (cholesterol-lowering) 2) PABA – inhibits Pteroyl Synthase (antibiotic) 3) Captopril – inhibits ACE (antihypertensive) 4) Oxamate – inhibits Lactate Dehydrogenase (poison) 5) […]
Types of Enzyme Inhibition with Mnemonics Read More »