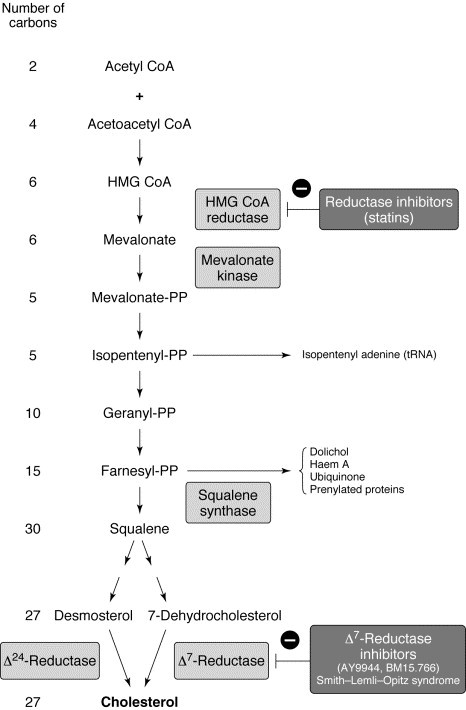
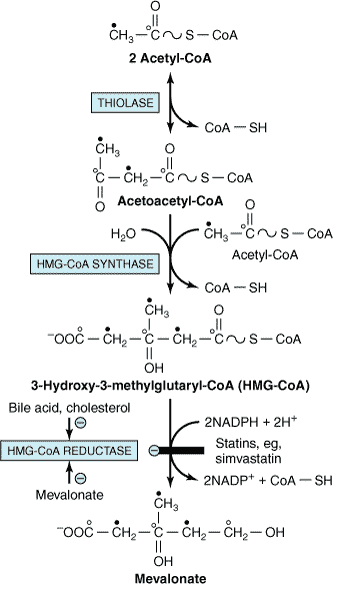
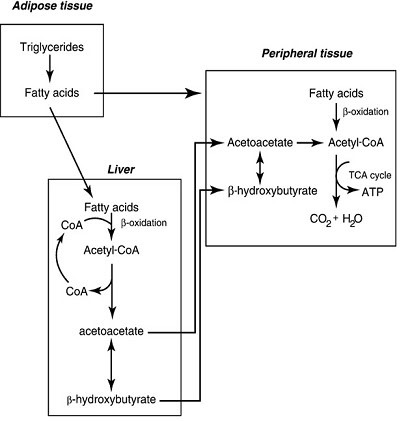
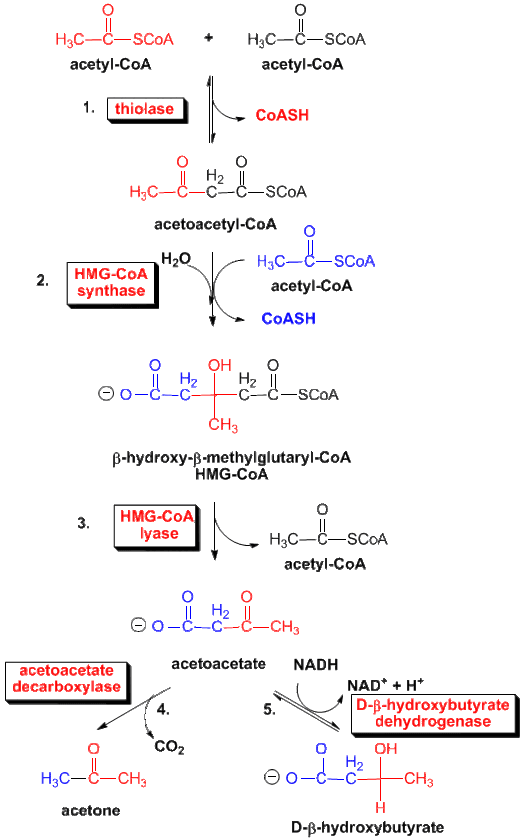
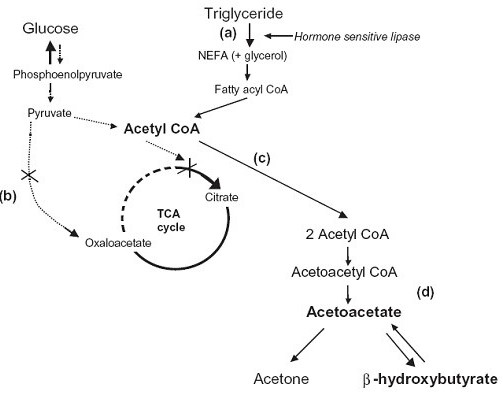
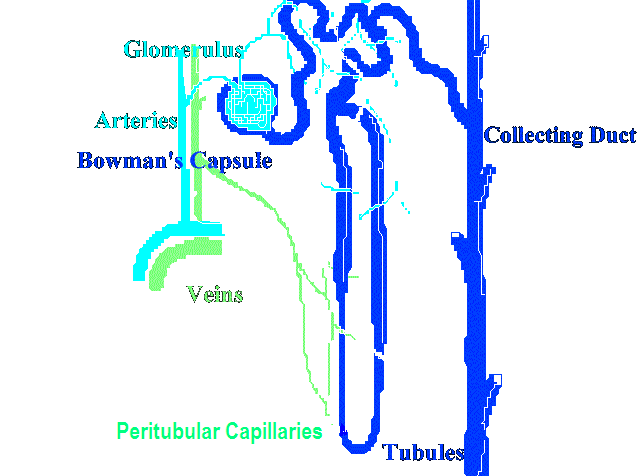
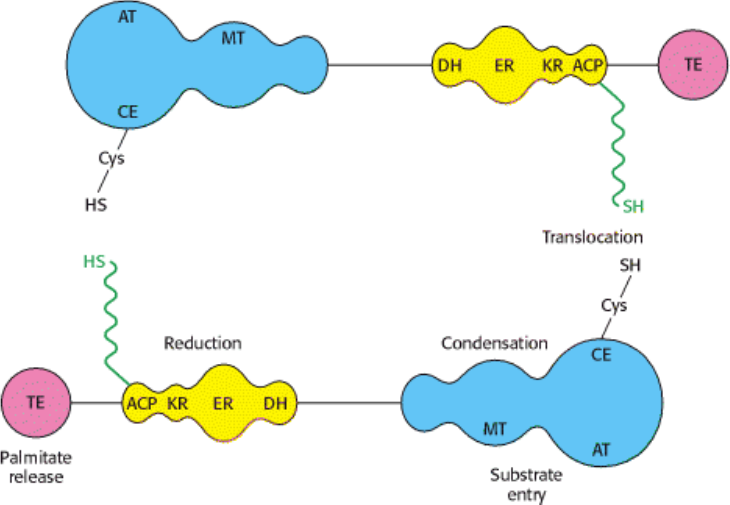
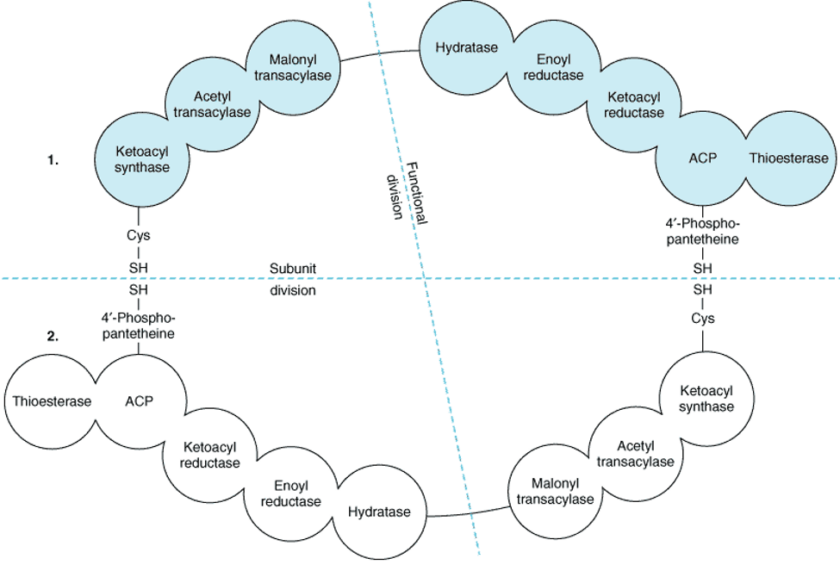
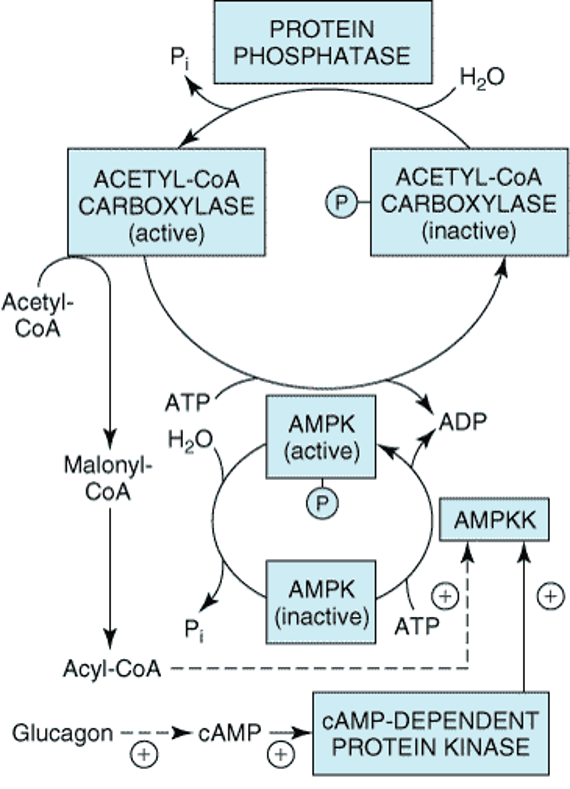
The reaction catalyzed by HMG Co-A Reductase
Case Details A 40-year-old man presents with chest pain that radiates to his left jaw and shoulder. He is diagnosed with a myocardial infarct (heart attack) and is prescribed statin medication. Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG CoA reductase, which converts HMG Co A to which of the following? Isopentenyl pyrophosphate Mevalonate Geranyl pyrophosphate Farnesyl […]
The reaction catalyzed by HMG Co-A Reductase Read More »