Beta oxidation of odd chain and unsaturated fatty acids- lecture-4
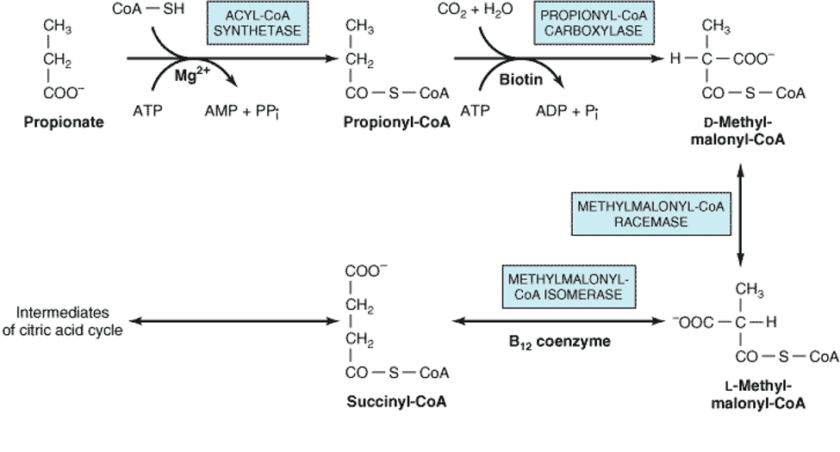
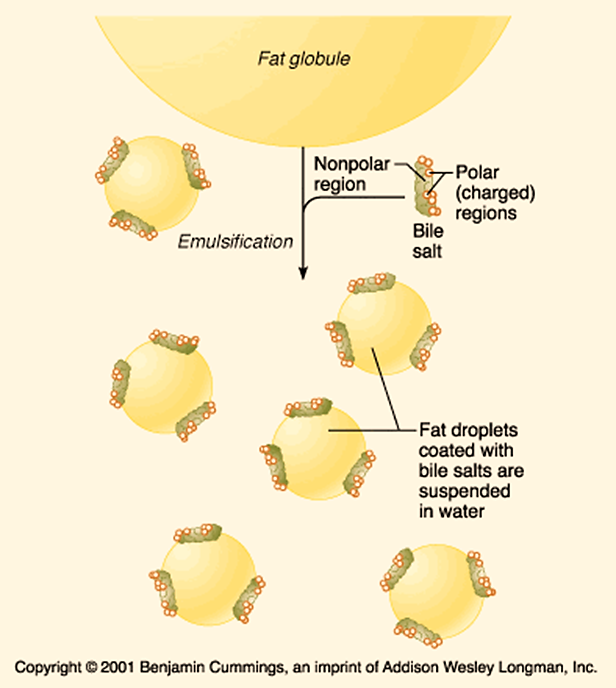
Fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms are oxidized by the pathway of β-oxidation, producing acetyl-CoA until a three-carbon (propionyl-CoA) residue remains. The 3- Carbon Propinyl CoA is utilized in the following way: The fate of propionyl CoA This compound is converted to succinyl-CoA, a constituent of the citric acid cycle (Figure 1). […]
Beta oxidation of odd chain and unsaturated fatty acids- lecture-4 Read More »