Minor pathways of oxidation of fatty acids- Lecture-2 (omega and peroxisomal oxidation)
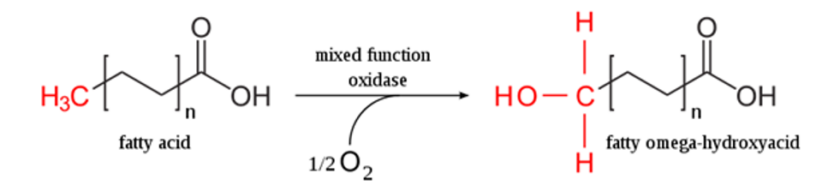
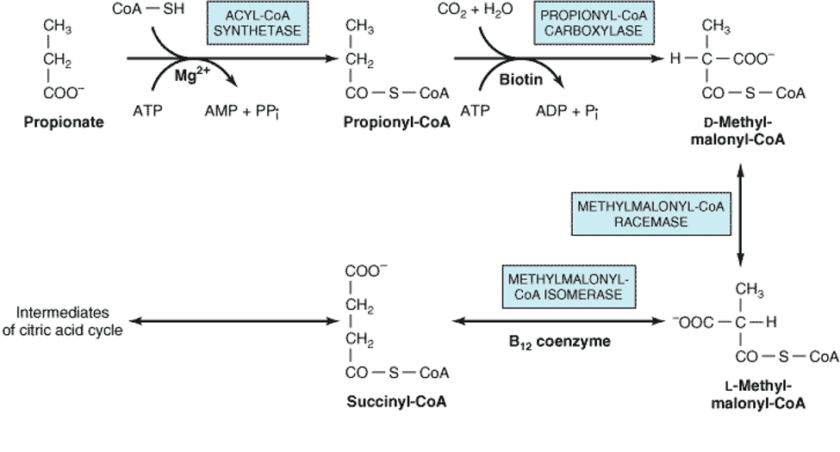
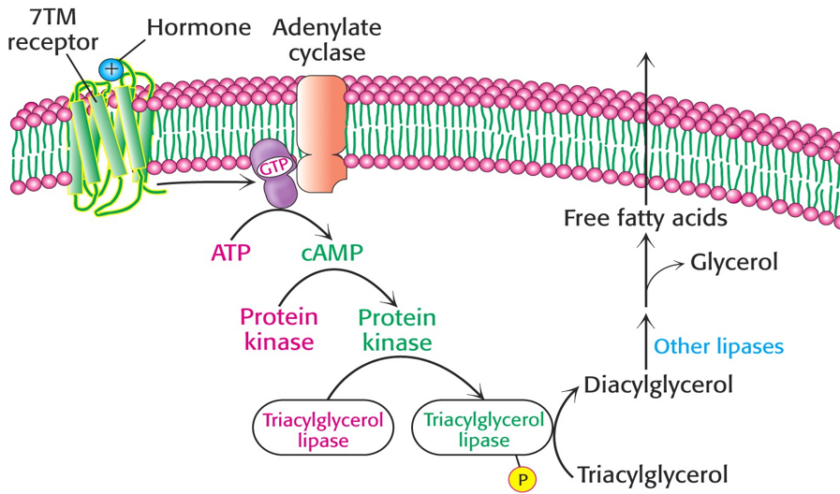
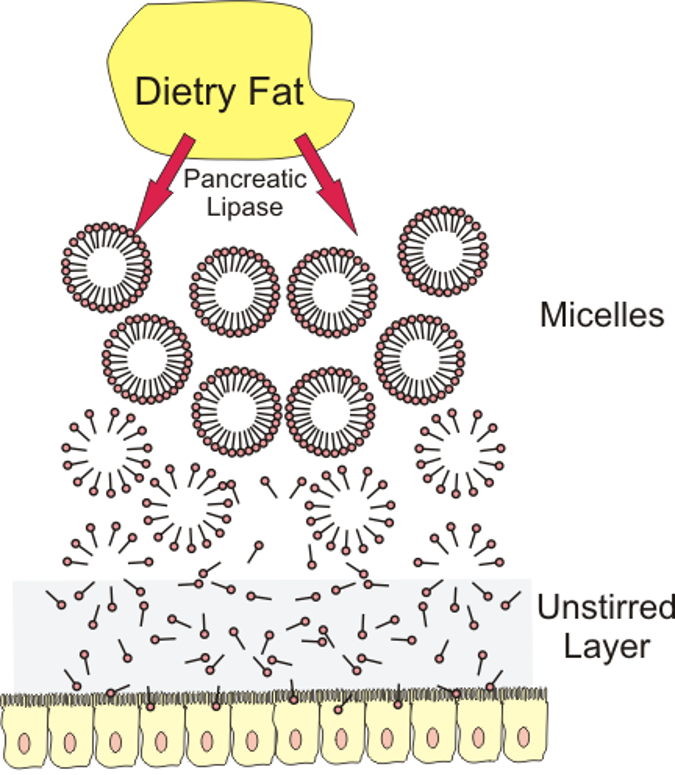
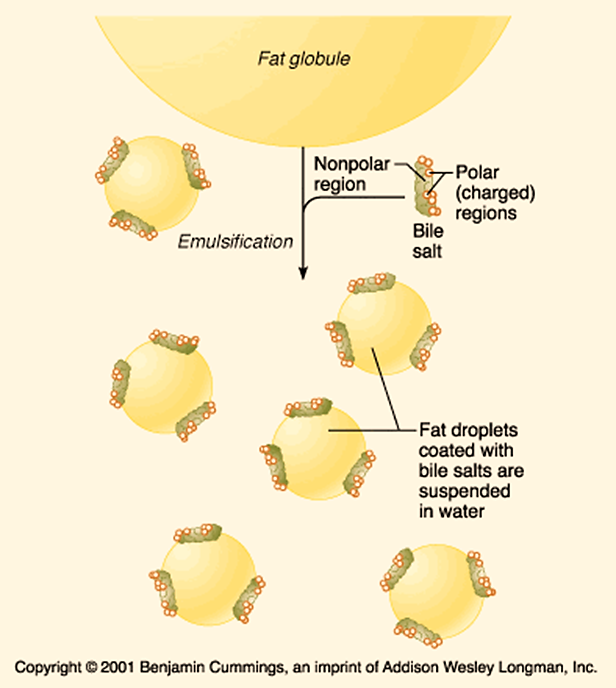
Omega oxidation of fatty acids Another minor pathway for fatty acid oxidation also involves hydroxylation and occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum of many tissues. In this case, hydroxylation takes place on the methyl carbon at the other end of the molecule from the carboxyl group or on the carbon next to the methyl end. It […]
Minor pathways of oxidation of fatty acids- Lecture-2 (omega and peroxisomal oxidation) Read More »